When tackling tough drilling tasks, cobalt and titanium drill bits often come into the conversation. Both offer advantages over standard high-speed steel (HSS) bits, particularly in terms of hardness and heat resistance. However, they achieve these benefits through different compositions and coatings, leading to distinct performance characteristics and ideal applications.
Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right drill bit for your project. Cobalt bits, with their uniform alloy composition, offer superior heat resistance throughout the bit. In contrast, titanium bits feature a thin coating that enhances surface hardness and reduces friction. Let’s delve deeper into their specific strengths and weaknesses.
What Are Cobalt Drill Bits
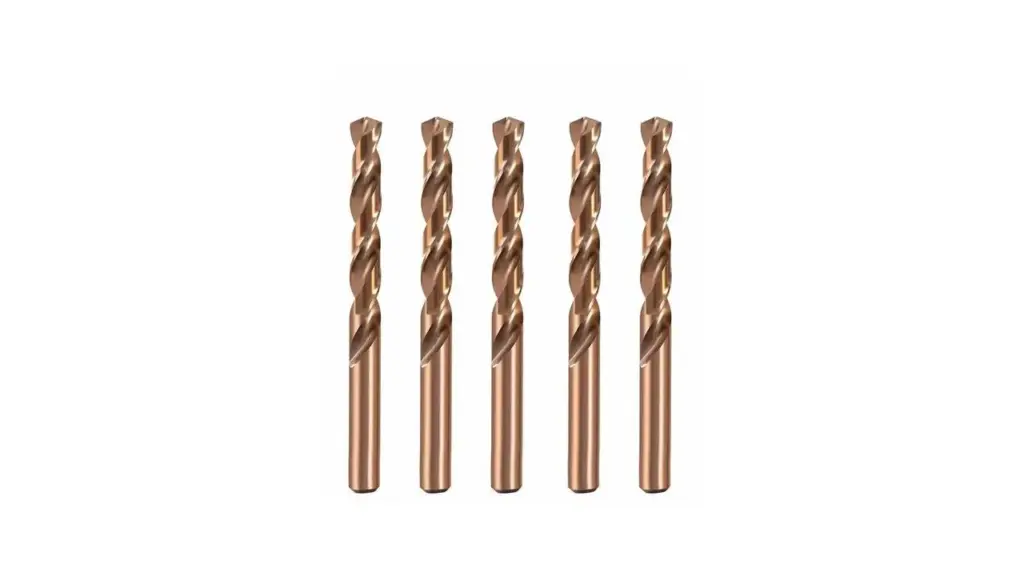

Cobalt drill bits are a type of high-speed steel (HSS) drill bit alloyed with 5 to 8 percent cobalt. This addition significantly increases the bit’s hardness, strength, and, most importantly, its heat resistance. The high heat resistance allows cobalt drill bits to maintain their sharpness even at higher temperatures generated when drilling through tough materials.
Consequently, they are exceptionally well-suited for drilling into hard metals such as stainless steel, cast iron, titanium, and other tough alloys, where standard HSS bits might quickly dull or fail. While more expensive than regular HSS bits, their extended lifespan and ability to cut through challenging materials make them a cost-effective choice for demanding applications.
What Are Titanium Drill Bits
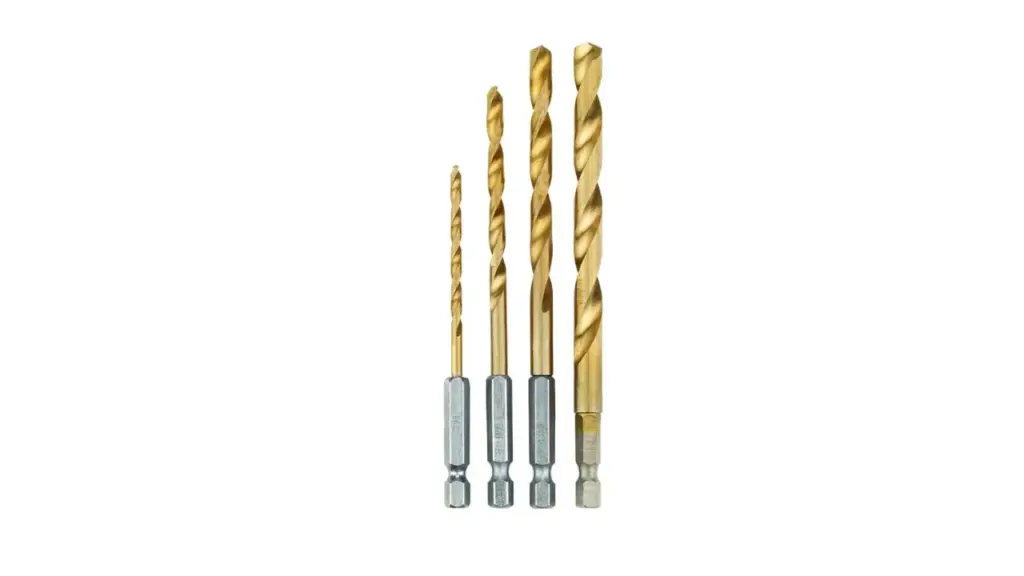

Titanium drill bits are high-speed steel (HSS) bits coated with titanium nitride (TiN), a hard ceramic material identifiable by its distinct gold color. This coating significantly enhances the drill bit’s surface hardness, reduces friction, and increases heat resistance compared to standard HSS bits.
As a result, titanium drill bits offer improved durability and can maintain their sharpness for a longer period when drilling through materials like wood, plastic, and softer metals such as aluminum and copper. While they are generally more cost-effective than cobalt drill bits, the titanium coating can wear off with use and cannot be effectively resharpened, limiting their lifespan in very demanding applications or when drilling harder metals.
Cobalt vs Titanium Drill Bits
What is the difference between cobalt and titanium drill bits?
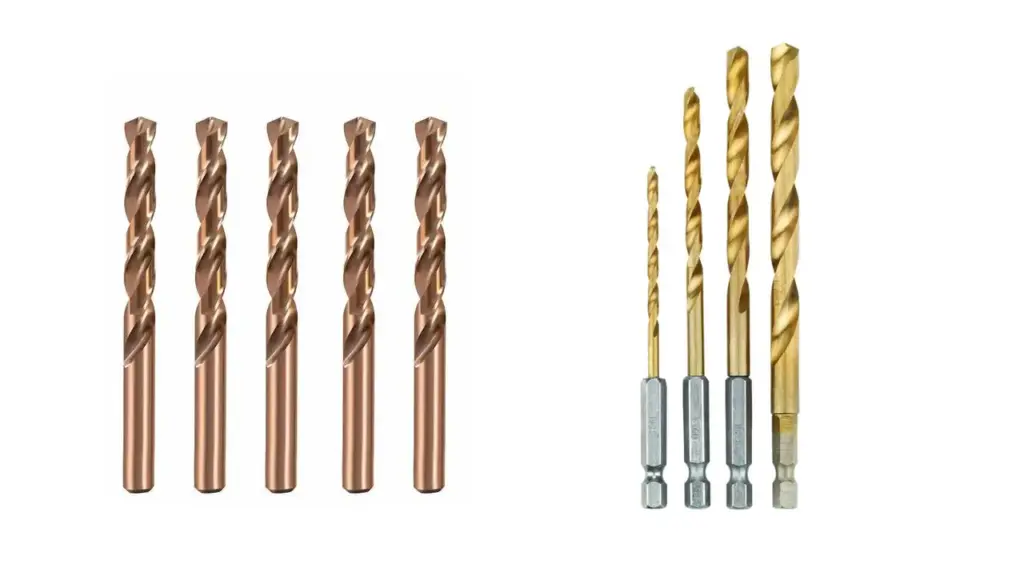

Choosing the right drill bit is crucial for efficient and effective drilling. Cobalt and titanium drill bits are popular choices offering distinct advantages. Cobalt drill bits, alloyed with cobalt, excel in high-heat applications and hard materials. Titanium drill bits, coated with titanium nitride, offer enhanced hardness and reduced friction for general-purpose drilling.
Understanding their differences will help you select the optimal bit for your specific needs.
Material and Construction
Cobalt drill bits are manufactured from high-speed steel that has been alloyed with cobalt, typically ranging from 5% to 8%. This integral composition provides uniform hardness and heat resistance throughout the entire bit. This means that even as the bit is resharpened, it retains its superior performance characteristics, making it ideal for demanding tasks. The inherent strength of the cobalt alloy allows these bits to withstand higher drilling temperatures without losing their temper or sharpness, ensuring a longer lifespan when working with tough materials.
Titanium drill bits, in contrast, are typically made from standard high-speed steel and then coated with a thin layer of titanium nitride (TiN). This coating is what gives the bits their characteristic gold color and provides increased surface hardness and reduced friction. While the coating enhances initial performance and extends the bit’s life compared to uncoated HSS bits, the underlying steel does not possess the same inherent heat resistance as cobalt. Once the titanium nitride layer wears off through prolonged or aggressive use, the bit’s performance will revert to that of a standard HSS bit.
Performance and Application
Cobalt drill bits are specifically designed for drilling through hard and abrasive materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, titanium, inconel, and other tough alloys. Their exceptional heat resistance allows them to maintain a sharp cutting edge even under the high temperatures generated when working with these materials. This makes them a preferred choice for professional machinists, metalworkers, and anyone who frequently drills into challenging metals where standard bits would quickly fail. The robust nature of cobalt bits also makes them suitable for drilling at higher speeds and feed rates, increasing efficiency in demanding applications.
Titanium drill bits are more versatile and are well-suited for general-purpose drilling in softer materials like wood, plastic, aluminum, copper, and mild steel. The titanium nitride coating reduces friction, allowing for smoother and cooler drilling, which helps to prolong the bit’s sharpness compared to uncoated HSS bits. They offer a good balance of performance and affordability for a wide range of DIY and light industrial tasks. However, they are not recommended for very hard or abrasive materials where the coating can quickly wear away, diminishing their advantage over standard HSS bits.
Cost and Longevity
Cobalt drill bits are generally more expensive than titanium drill bits due to the higher cost of the cobalt alloy and the more complex manufacturing process. However, their superior durability and ability to maintain sharpness when drilling hard materials often translate to a longer overall lifespan in demanding applications. For professionals who frequently work with tough metals, the increased initial investment in cobalt bits can be offset by their extended use and reduced need for frequent replacements.
Titanium drill bits are typically more budget-friendly, making them an attractive option for general-purpose drilling needs. While the titanium coating enhances their lifespan compared to uncoated HSS bits, they may not last as long as cobalt bits when used consistently on hard or abrasive materials. For occasional drilling in softer materials, titanium bits offer a cost-effective upgrade. However, for heavy-duty applications involving hard metals, the long-term value and performance of cobalt bits often justify their higher price.
| Feature | Cobalt Drill Bits | Titanium Drill Bits |
| Material | HSS alloyed with 5-8% Cobalt | HSS with Titanium Nitride (TiN) Coating |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, maintains sharpness at high temperatures | Good, coating reduces heat but underlying steel is standard HSS |
| Hardness | High, uniform throughout the bit | High surface hardness due to coating, underlying steel is standard HSS |
| Friction | Moderate | Low due to the coating |
| Best For | Hard metals (stainless steel, cast iron, titanium) | Softer metals, wood, plastic, general-purpose drilling |
| Durability | Excellent, long lifespan in demanding applications | Good, but coating can wear off, limiting lifespan in hard materials |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Generally less expensive |
| Resharpening | Retains performance after resharpening | Performance decreases once coating wears off |
Black Oxide vs Titanium vs Cobalt Drill Bits
Choosing the right drill bit for your project impacts efficiency and the longevity of the bit itself. Black oxide, titanium, and cobalt drill bits are common options, each with unique characteristics. Black oxide offers a basic level of protection and is suitable for general use.
Titanium-coated bits provide increased hardness and reduced friction, while cobalt drill bits excel in demanding applications involving hard metals due to their superior heat resistance. Understanding their fundamental differences will guide you in selecting the most appropriate drill bit for your specific material and drilling needs.
Material and Construction
Black oxide drill bits are produced by treating standard high-speed steel (HSS) with a black oxide finish. This chemical process creates a thin, porous layer on the surface of the bit, offering mild corrosion resistance and slightly improved lubricity compared to uncoated HSS. The black oxide layer is relatively thin and does not significantly enhance the bit’s hardness or heat resistance. These bits are generally the most economical option and are suitable for general-purpose drilling in softer materials.
Titanium drill bits are also typically made from HSS but are distinguished by a thin coating of titanium nitride (TiN). This coating is significantly harder than the black oxide finish and reduces friction between the bit and the workpiece. The titanium nitride layer helps the bit stay sharper for longer when drilling materials like wood, plastic, and softer metals. However, like black oxide, the coating is only on the surface, and the underlying HSS does not have enhanced heat resistance. Once the coating wears off, the bit’s performance will be similar to that of a standard HSS bit.
Cobalt drill bits differ fundamentally as they are made from an HSS alloy that includes 5% to 8% cobalt throughout the entire bit. This integral alloying provides a significant increase in hardness and, crucially, heat resistance compared to both black oxide and titanium-coated bits. Because the cobalt is part of the metal matrix, the bit retains its performance characteristics even after resharpening. This construction makes cobalt bits ideal for drilling hard and abrasive materials where high temperatures are generated.
Performance and Application
Black oxide drill bits are best suited for drilling into softer materials such as wood, soft plastics, and non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper. They offer a decent performance for general DIY tasks and basic metalworking where extreme hardness or heat resistance is not required. While they can drill mild steel, they may dull relatively quickly compared to titanium or cobalt bits, especially with frequent use.
Titanium drill bits offer improved performance over black oxide bits in a wider range of materials, including hardwood, fiberglass, PVC, and various steels. The reduced friction and increased surface hardness allow for smoother drilling and a longer cutting life in these applications. They are a good middle-ground option for users who need more durability than black oxide but may not frequently work with extremely hard metals.
Cobalt drill bits are the top performers when it comes to drilling hard and tough materials like stainless steel, cast iron, titanium alloys, and hardened steel. Their superior heat resistance allows them to maintain a sharp cutting edge at high drilling temperatures, preventing premature dulling and failure. They are the preferred choice for professionals in metalworking, machining, and construction who regularly encounter challenging drilling tasks.
Cost and Longevity
Black oxide drill bits are the most cost-effective option upfront, making them attractive for users with basic drilling needs and budget constraints. However, their lifespan may be shorter, especially when used on harder materials, potentially leading to more frequent replacements.
Titanium drill bits are typically more expensive than black oxide bits but offer a better balance of performance and cost for general-purpose use. Their increased durability due to the titanium coating can extend their lifespan compared to black oxide bits, making them a worthwhile upgrade for many users.
Cobalt drill bits represent the highest initial investment among these three types. However, their exceptional durability and ability to effectively drill hard materials often result in a longer service life in demanding applications. For professionals, the reduced need for frequent replacements and the ability to handle tough jobs efficiently can make cobalt bits the most cost-effective choice in the long run. When considering wholesale drill bits from Sinodrills, evaluate the trade-offs between initial cost and long-term performance based on your intended applications.
| Feature | Black Oxide Drill Bits | Titanium Drill Bits | Cobalt Drill Bits |
| Material | HSS with a black oxide surface finish | HSS with a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating | HSS alloyed with 5-8% Cobalt throughout |
| Heat Resistance | Low | Moderate, coating helps reduce heat | Excellent, maintains sharpness at high temperatures |
| Hardness | Basic HSS hardness | Increased surface hardness due to coating | High, uniform hardness throughout the bit |
| Friction | Moderate | Low due to the coating | Moderate |
| Best For | Soft wood, plastic, non-ferrous metals, light use | Wood, most metals, general-purpose drilling | Hard metals (stainless steel, cast iron, titanium alloys) |
| Durability | Lowest lifespan, especially on harder materials | Longer lifespan than black oxide, coating can wear off | Longest lifespan in demanding, high-heat applications |
| Cost | Least expensive | Moderately expensive | Most expensive |
| Resharpening | Standard HSS performance after resharpening | Standard HSS performance after coating wears off | Retains performance characteristics after resharpening |
Are Cobalt Drill Bits Better Than Titanium
Determining whether cobalt drill bits are definitively “better” than titanium drill bits depends heavily on the specific application and the materials being drilled. Neither type is universally superior; each offers distinct advantages that make them suitable for different tasks.
Cobalt drill bits generally offer superior performance in the following aspects:
- Hardness: The cobalt alloy provides inherent hardness throughout the bit, making it excellent for drilling very hard materials like stainless steel, cast iron, and titanium.
- Heat Resistance: Cobalt’s high melting point allows these bits to withstand higher temperatures generated during demanding drilling tasks without losing their sharpness.
- Durability in Hard Materials: Due to their inherent hardness and heat resistance, cobalt bits tend to last longer when consistently drilling tough metals.
- Resharpening: Cobalt bits retain their performance characteristics even after resharpening because the material composition is consistent throughout.
Titanium drill bits, on the other hand, offer benefits in different scenarios:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Titanium-coated bits are generally less expensive than solid cobalt bits, making them a more budget-friendly option for many users.
- Performance in Softer Materials: They perform well in wood, plastic, and softer metals like aluminum and copper, offering a good balance of sharpness and durability for these applications.
- Reduced Friction: The titanium nitride coating lowers friction during drilling, which can lead to smoother and cooler operation in appropriate materials.
- Initial Sharpness: A new titanium-coated bit can often feel sharper initially for general-purpose drilling compared to a standard HSS bit.
Ultimately, the “better” drill bit depends on your needs. If you frequently drill into hard metals and prioritize longevity and performance in demanding applications, cobalt drill bits are likely the better choice. If you primarily work with softer materials and are looking for a more affordable and versatile option for general use, titanium drill bits can be a very good solution.
How to Choose Cobalt and Titanium Drill Bits
Selecting the appropriate cobalt or titanium drill bit hinges on the specific materials you intend to drill and the demands of your project. Cobalt drill bits, with their inherent hardness and exceptional heat resistance, are the superior choice for drilling into tough and abrasive materials like stainless steel, cast iron, hardened steel, and titanium alloys.
Their ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge at high temperatures ensures efficient material removal and a longer lifespan when working with these challenging metals. If your work frequently involves such materials, investing in cobalt drill bits will likely prove more cost-effective in the long run due to their durability and performance.
Titanium drill bits, characterized by their titanium nitride coating, offer enhanced hardness and reduced friction compared to standard high-speed steel bits. They are a versatile option suitable for drilling into a wider range of materials, including wood, plastic, softer metals like aluminum and copper, and mild steel.
While they provide improved performance and longevity over uncoated HSS bits in these applications, the titanium coating can wear off when drilling very hard or abrasive materials, diminishing their advantage. Therefore, if your drilling tasks primarily involve softer materials and occasional work with mild steel, titanium drill bits can offer a good balance of performance and affordability.
Consider these factors when choosing between cobalt and titanium drill bits:
- Material Hardness: For very hard metals (stainless steel, hardened steel), cobalt is the preferred choice. For softer materials (wood, aluminum), titanium can suffice.
- Heat Generation: If your drilling process generates a lot of heat (due to material hardness or high speed), cobalt’s superior heat resistance is crucial.
- Frequency of Use: For frequent drilling into tough materials, the durability of cobalt bits justifies the higher cost. For occasional use on softer materials, titanium bits may be adequate.
- Budget: Titanium bits are generally more affordable upfront, but cobalt bits may offer better long-term value for demanding applications.
- Hole Precision and Finish: Both types can provide good results, but maintaining sharpness (especially with cobalt on hard metals) contributes to cleaner holes.
- Drill Speed and Feed Rate: Cobalt bits can often handle higher speeds and feed rates when drilling hard materials due to their heat resistance.
Conclusion
In summary, cobalt drill bits excel in drilling hard metals due to their superior heat resistance and inherent hardness, making them a worthwhile investment for metalworking. Titanium-coated bits offer improved performance over standard HSS for softer materials by reducing friction and heat. However, the coating can wear off with demanding use.
For drilling into abrasive materials like hardened steel or stainless steel, cobalt bits are the preferred choice due to their consistent hardness throughout the bit. Titanium bits are a cost-effective upgrade for general-purpose drilling in wood and softer metals, offering a balance of performance and price.
When sourcing drill bits wholesale, consider Sinodrills for a range of options. Evaluate your primary drilling applications to determine whether the superior heat resistance of cobalt or the enhanced lubricity of titanium best suits your needs and budget.